High-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) is an advanced form of liquid chromatography used to separate the components of a mixture. The mixture is dissolved in a solvent (mobile phase) and then forced to flow through a chromatography column under high pressure. In the column, the mixture is resolved into components.
1- High-speed liquid chromatography. The separation is completed within a few minutes.
2- High-performance liquid chromatography.
3- High-resolution liquid chromatography
High performance is the result of many factors: Smaller particles of the stationary phase, uniform pore size, high-pressure column slurry packing techniques, accurate low volume of the sample injected, sensitive detector, and good pump system.
{tocify} $title={Table of Contents}
The separation occurs because each component in the mixture interacts differently with the stationary phase (Yellow component) will move slowly through the column, while the molecules that interact less strongly (blue component) will move rapidly through the column.
In HPLC the stationary phase has two characters:- has a small particle size (5.0 - 10.0 µm). and packed under high pressure.
Reduction of the particle size of the stationary phase leads to:- Leaving less apace for the mobile phase to pass through. Decrease the flow rate of the liquid mobile phase. Thus pressure from 1000 - 5000 psi, pound per square inch (68 - 340 atom.) is applied to overcome the obstructive of fine particles.
Classification of Chromatography (HPLC)
Types of HPLC according to the mechanism of separation. 1. Adsorption chromatography 2. Size exclusion chromatography. 3. Ion exchange chromatography.
1. Adsorption chromatography
The stationary phase is an adsorbent and the separation is based on adsorption-desorption steps.
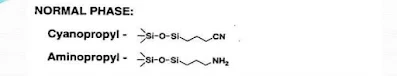
(A) Normal phase chromatography:- The stationary phase is strongly polar (e.g. silica gel) and the mobile phase is non-polar such as (hexane or tetrahydrofuran). The polar sample retained longer on the column.
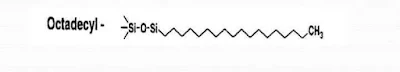
(B) Reversed-phase chromatography:- The stationary phase is strongly non-polar (e,g. C18 silica, hydrophilic) while the mobile phase is polar (as a mixture of water and methanol or acetonitrile).
2. Size exclusion Chromatography
The column is packed with material having controlled pore size and the sample is screened or filtered according to its molecular sizes, there is no interaction between the solute and stationary phase. The large molecules rapidly wash through of column, and the smaller molecules penetrate inside the pores and elute later.
3. Ion exchange chromatography
The stationary phase has an ionically charged surface of opposite charge to the sample ions. This technique is used only for ionic or ionizable samples.
Type of ion exchange (Type of Standard pH):- (i) Anion exchange resin (ii) cation exchange resin Matrix:- is a polymer of styrene with divinylbenzene.
(i) Anion exchange: strong anion as quaternary ammonium from the matrix- (NR3)+ --- Cl-, weak anion as a matrix- NH2(CH3)-CL-
(ii) Cation exchange: strong cation, sulfonic acid matrix- (SO3)- H+, weak cation, matrix-COO- H+ The stronger the charge on the sample, the stronger it will be attached to the ionic surface and thus the longer it will take to elute. The mobile phase is an aqueous buffer, where the pH is adjusted to control elution times.
Used of HPLC
HPLC can be divided into two main types according to uses.
1.0 Analytical types: which is used. In identification and assay (purity) of components in a mixture and to know the numbers of components in a mixture.
2.0 Preparative or semipreparative type: used in isolation and purification.
The difference between analytical and preparative HPLC.
Analytical HPLC:- Dimension of column 1.0-6.0 mm. i.d. For analytical HPLC pumps should have a flow rate that ranges from 1-10 ml/min. The injected volume of the sample in analytical HPLC ranges from 20 uL to 1.0 ml.
Preparative HPLC:- Dimensions of column up to 3 cm i.d.For preparative HPLC flow rate in excess of 100 ml/min. In preparative or semi-preparative HPLC volume of the sample from 1.0 ml to 5.0 ml or more.
Chromatography Process
The process begins by Injecting the solute into the column (0 time). The separation occurs as the analyte and mobile phase are pumped through the column. Detection of components by detector is displayed on a chart or computer screen.
Some Important Compounds of Copper | Copper Compounds and Uses
Advantages of HPLC
1. High speed
2. High resolution
3. High sensitivity
4. Re-usable column
5. No destruction of the component
6. The instrumentation is automatic, computerized
7. Quantitative work is more easily and most sensitive
8. The sample is recovered completely.
Application of HPLC
1. Isolation and purification of biologically active natural products
2. Control of synthetic reactions, identification of intermediates and target compound
3. Detection of bio-genetic intermediates and enzymes involved.
4. Control of the microbiological process, Used for the separation of an antibiotic from the broth mixture.
>Biochemistry and bsc biochemistry | Fundamentals of biochemistry