Drying refers to an operation (process) in which the moisture of a substance (usually solid) is removed by thermal means (i. e. with the help of thermal energy).
Drying usually refers to the removal of relatively small amounts of water from a solid or nearly solid material. It involves the transfer of liquid from a wet solid into the unsaturated gas phase (drying medium).
Chemical Drying Process
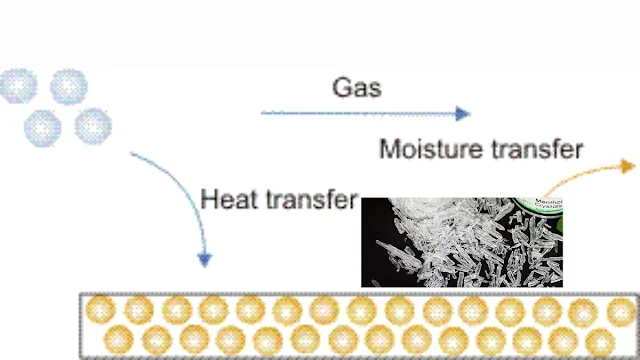
During drying, operation mass and heat transfer occur simultaneously. Heat is transferred from the bulk of the gas phase (drying medium) to the solid phase and mass is transferred from the solid to the gas phase in the form of liquid and vapor through various resistances. The material that is transferred is the solute and transfer takes place as the gas phase is always unsaturated with respect to the solute material.
{tocify} $title={Table of Contents}
> Tray dryer Principle construction and working
In drying, relatively small amounts of water or other liquid are removed from a solid or semi-solid material (using thermal energy) whereas, in evaporation, a relatively large amount of water is removed from the solutions. Drying involves the removal of water at a temperature below the boiling point, while evaporation involves the removal of water as a vapor at its boiling point. Drying involves the circulation of hot air or other gas over a solid material for the removal of water while in evaporation use of steam heat is done for the removal of water. To obtain the products almost in the dried form is the purpose of the drying operation, whereas the concentration of the solution is the main purpose of evaporation.
As the removal of moisture by thermal means is more costly than mechanical means (filtration), the moisture content of the solids must be reduced to the minimum possible level by the latter means before the material is fed to drying equipment.
In most drying operations, the heat is provided by hot air or any other gas-drying medium. Drying is frequently the last operation in the manufacturing process and is usually carried out after evaporation, filtration, or crystallization.
Drying operations are mostly used in the food, chemical, agricultural, pharmaceutical, and textile industries.
Advantages of Drying Operation/Process
The drying operation is carried out for several reasons given below:-
(i) For reducing the transport cost.
(ii) For purifying a crystalline product so that the solvent adhering to crystals is removed.
(iii) For making the material more suitable for handling and storage. Handling and storage of dry solids are easy.
(iv) To meet the market specifications of solid products set by the customers.
(v) For providing definite properties to materials
(vi) In some cases to prevent corrosion arising due to the presence of moisture. Dry chlorine gas is not corrosive but traces of moisture make it very corrosive.
(vii) Sometimes it is an essential part of the process (e.g. drying of paper in paper marking).
Factors on which the rate of drying depends
(A) Gas velocity: When the velocity of the gas or air is high, the rate of drying will also be high.
(B) Humidity of gas: The lower the relative humidity, the more will be the rate of drying.
(C) Area of drying surface: If the area of the wet surface exposed to the gas or air is more the rate of drying will also be higher.
(D) Temperature: If the temperature of the gas is increased, its relative humidity decreases and thus increases a driving force so the rate of drying increases.
Time of drying under constant conditions
Consider that the wet solids are to be dried by passing the hot air over them under constant drying conditions. The time of drying required to dry the material from the initial moisture to the moisture content of solids is the sum of the time required during the constant rate period and the time required during the falling rate period.
Properties of the air-water system
The moisture removed during the drying operation gets added to the hot gas or air which in turn depends upon the temperature and humidity of the gas or air. Usually, in drying operations, hot air is used as a drying medium, so it is essential to know some of the properties of the air-water system.
Take these Notes is, Orginal Sources: Unit Operations-II, KA Gavhane