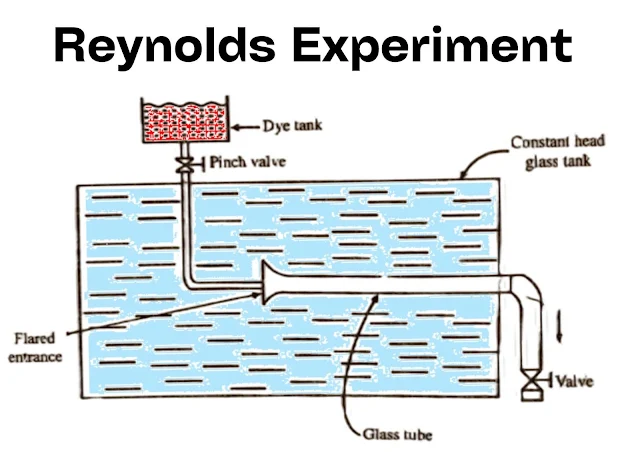
Sir Osborne Reynolds expressed the difference between these two flows (laminar and turbulent) through his experiments, which are called Reynolds Experiments.
When liquid flows through tubes and pipes, we can express it in two parts in terms of state.
(i) Laminar flow and
(ii) Turbulent Flow.
Theory of Reynolds Experiment
Reynolds's experiment is shown in the figure. Due to this, a glass tube is attached directly to the outlet in a tank, in which the liquid output is controlled with the help of a valve. The fluid from the hose is collected in a discharge tank for the time being by the stopwatch. From which the precipitate is calculated, a dyeing liquid is released by a separate arrangement at the entrance of the glass tube so that the water level in the tank is kept constant.
Some water particles will be colored by the substance and the velocity of their flow is taken, it has been seen from the experiment that when the speed is low, a colored needle is seen flowing directly in the glass tube. When the velocity increases, this needle becomes suspended in place of the velocity, and the whole water becomes colored.
Reynolds Experiment Results
Reynolds derived the result that when the velocity reaches the critical value, the streamlines start becoming wavy, due to which the needle also becomes wavy. When the velocity increases further, the flow becomes turbulent, due to which the water particles dissolve and mix the color completely in the water.
Reynolds Number - Definition, Formula, and Limit
Definition: Reynolds experimented to find out under which conditions one type of flow is converted into another type of flow. According to Reynolds, the critical velocity at which laminar flow changes into turbulent flow depends on the diameter of the pipe (d), the density (ρ) of the flowing liquid, the velocity (V) of the liquid, and its viscosity (μ).
On this basis, Reynolds gave a Unitless formula that expresses a number, called the Reynolds Number, the Reynolds number is denoted by the NRe.
Reynolds Number = ρ. V. d/(μ)
r = (μ)/ρ we know
ρ/(μ) = 1/r
NRe = V.d/r
Where r is the constant of critical viscosity.
Laminar and turbulent flow Reynolds number
Below 2000, the flow is laminar.
Flows greater than 4000 are turbulent.
The flow is erratic between 2000 to 4000.
Velocity values at 2000 are lower equatorial velocities.
Exctical velocities above the value of the velocity at 4000.
Also Read: Bernoulli's Theorem Definition, Derivation, and Applications