In fluid mechanics, specific gravity refers to the weight of a fluid per unit volume. It is denoted by γ (gamma). The specific gravity is calculated by the following formula:
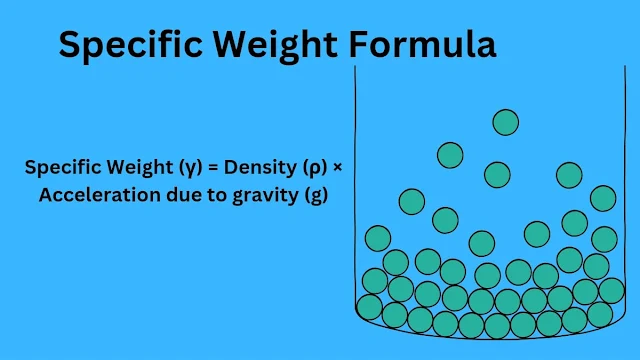
Specific Weight (γ) = Density (ρ) × Acceleration due to gravity (g)
Where
- Density (ρ) is the mass of the fluid per unit volume.
- Acceleration due to gravity (g) is the gravitational acceleration is 9.81 m/s² on Earth.
Depending on the units used for density and acceleration due to gravity, the unit of specific mass is the N/m³ or lb/ft³.
For example
If we have water with a density of 1000 kg/m³, we can calculate its specific gravity as γ = 1000 kg/m³ × 9.81 m/s² ≈ 9810 N/m³
The specific gravity of water would be 9810 N/m³.
Density from Specific Gravity
Density and specific gravity are related to each other but they are different terms. Specific gravity is a dimensionless quantity that compares the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance (usually water) at a specified temperature and pressure.
To calculate density from specific gravity, the specific gravity of the substance and the density of a reference substance (water) must be known. To convert specific gravity to density, use this formula:
Density = Specific Gravity × Density of Reference Substance
Specific Weight in Fluid Mechanics
Specific gravity refers to the weight of a liquid per unit volume. It is defined as the force exerted by gravity on a unit volume of a fluid. The specific gravity is denoted by γ (gamma).
Specific Weight (γ) = Weight (W) / Volume (V)
Where
- Weight (W) is the force exerted by gravity on the fluid
- Volume (V) is the volume of the liquid.
The unit of specific weight depends on the units used for weight and volume.
- N/m³ (newtons per cubic meter) and lb/ft³ (pounds per cubic foot).
The Specific Weight of Water Formula
The specific gravity of water is the weight per unit volume of water. It is denoted by γ (gamma). Calculate the specific gravity of water using the following formula:
Specific Weight of Water Formula
(γ) = (ρ) × (g)
Where
- The density of water (ρ) is the mass of water per unit volume. Pure water density at 4 °C is 1000 kg/m³ or 62.43 lb/ft³.
- The acceleration due to gravity (g) is the acceleration due to gravity, which is 9.81 m/s² or 32.2 ft/s².
The Specific Weight of Water
It is important to note that these values are approximate and may vary slightly depending on factors such as temperature and impurities in the water.