The rate equation relates the rate of reaction to the concentrations of reactants and products scaled up to their respective reaction orders. Each term in this rate equation that involves the concentration of a reactant or product is called a concentration-dependent term.
Considering the following irreversible reaction
a.A +b.B ⟶ r.R +r.S
A is a reactant that is not present in the product of the reaction.
{tocify} $title={Table of Contents}
A acts as a base for calculating r. The rate of absent reactant\[ A (-r_A)\]depends on its temperature and composition. Many reactions can be written as the product of concentrations of species.
-r_A \ = k.F (C_A, C_B...........)
Where \[-r_A \] = Rate of Reactions concerning A.
\[F \ = (C_A, C_B...........)\] is a mathematical function of the above.
Where \[ (C_A, C_B............)\] is the concentration of A and B. But it is obtained from kinetics. The rate of reaction mainly depends on the concentration of reactants.
As \[-r_A\ = k.C^(nA)_A, C^(nB)_B...........\]
Where K is the Reaction rate constant nA, nB are the curves of concentrations of reactants A,B. On which the rate of reaction depends. It is not necessary that
\[nA = a\]
\[nB = b\]
The algebraic equation expresses the relationship between (-rA) and the concentrations of species participating in a reaction. Kinetic expansion is called rate loss or rate equation. Hence the rate of reaction reveals the relation between concentration and concentration.
FAQs
What is the Single Reaction?
When the progress of a reaction is shown by a single stoichiometric equation or single rate equation, it is called a signal reaction.
What is the Multi Reaction?
When more than one stoichiometric equation is used to progress a reaction, it is called a multiple reaction or complex reaction. It is of two types.
(i) Series Reaction
When one reactant is converted into a product and that product is converted into another product, this type of reaction is called a chain reaction.
\[ A ⟶ B ⟶ C\]
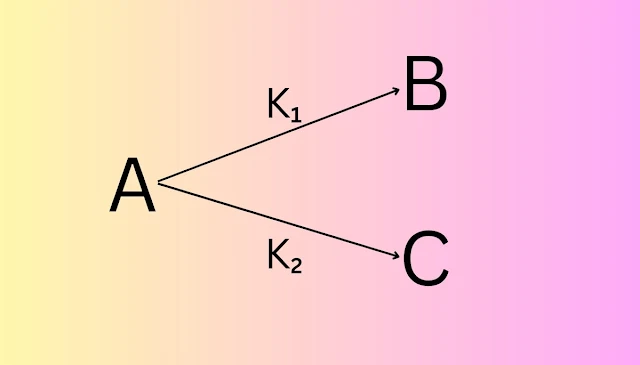
(ii) Parallel Reaction
When one reactant is converted into two different products by two different reactions, then this type of reaction is called a parallel reaction.